LOLgorithm: Humor Detection

- Humor is a fascinating and puzzling area of study in the field of computers understanding human language.
- ColBERT Dataset: The ColBERT dataset has 200,000 statements with humor labels and is accessible on Kaggle for model training and evaluation.For testing, r/jokes, a subreddit was scraped.
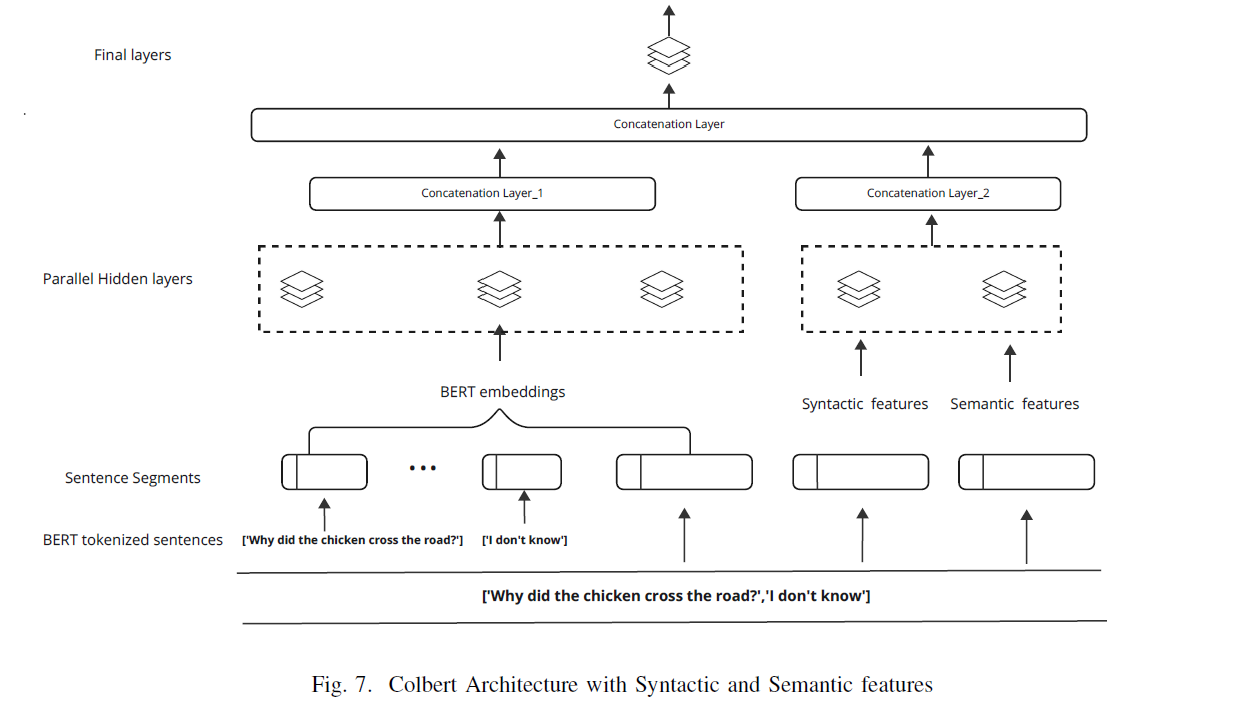
- The aim of this project was to understand how syntactic, semantic and contextual embeddings affect the performance of model and whether combining them together result into better model predictions.
- In this project, syntactic elements were captured with the help of NRCLex and NLTK libraries
- First component of syntactic elements was the statistics of 10 lexicons engineered for each joke.
- Second component of syntactic elements was the statistics of structural elements such as verb count, noun count, phrase length ratio, etc.
- The semantic elements were captures using NLTK and WordNet, CMUDict and were mostly based on humor theories (can be found in literature). The theories and formulae are as follows:
- Incongruity structure: To capture incongruous structure
- Disconnection: Representing the maximum meaning (semantic) distance among word pairs in a sentence.
- Repetition: Representing the minimum meaning (semantic) distance among word pairs in a sentence.
- Ambiguity theory: Humor is ambiguous, to capture this
- Sense Combination: This computation involves identifying Nouns, Verbs, Adjectives, and Adverbs through a POS tagger. Subsequently, we consider the potential meanings of these words (w1, w2, … ,wk) via WordNet, calculating the sense combinations
- Sense Farmost: the largest Path Similarity of any word senses in a sentence.
- Sense Closest: the smallest Path Similarity of any word senses in a sentence.
- Phonetic style: the phonetic characteristics of humorous sentences hold significant importance alongside their content
- Alliteration: quantifies the count and maximum length of alliteration chains within a sentence.
- Rhyme: measures the count and maximum length of rhyme chains.
- The Contexutal features were directly obtained by BERT embeddings.
- Used Decision Trees and SHAP to derive important features.
- These features were then pass to colBERT model separately and together to assess the performance.
- It was observed that combining all three features increased the prediction accuracy.